IUCN - The International Union for Conservation of Nature © IUCN - IUCN, A Key Partner for SDGs
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature)
©2021 IUCN, International Union for Conservation of Nature
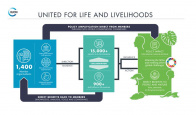
IUCN is a membership Union composed of both government and civil society organisations. It harnesses the experience, resources and reach of its more than 1,400 Member organisations and the input of more than 18,000 experts. This diversity and vast expertise makes IUCN the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. Active in 160+ countries.
Global Policy
 © IUCN
© IUCN
https://www.iucn.org/theme/global-policy/about
IUCN and SDGs
 © IUCN
© IUCN
IUCN, A KEY PARTNER FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
https://www.iucn.org/sites/dev/files/sdgs_-_uicn_-_web_-_eng.pdf
Harnessing the experience, resources and reach of its Members and experts, IUCN is the leading provider of conservation data, assessments and analysis, and an implementing agency of conservation projects around the world. IUCN champions nature’s role in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It also serves as an official agency monitoring progress towards biodiversity-related targets.
The 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda, and the 17 SDGs that underpin it, recognise that the natural world and its life-giving services must be urgently protected if we are to fulfil the needs of nine billion people by 2050.
The SDGs are premised on the notion that we cannot solve problems in isolation. For example, producing more food for the growing human population (SDG 2) will require freshwater supplies for adequate irrigation (SDG 6). The availability of freshwater will depend on healthy ecosystems (SDGs 14 and 15), which are increasingly impacted by climate change (SDG 13). Protecting these ecosystems will require strong institutions, governance and cooperation from the local to the international level (SDGs 16 and 17).
https://www.iucn.org/theme/global-policy/our-work/sustainable-development-goals/iucn-and-sdgs
SDG 15
Sustainable management of terrestrial ecosystems helps mitigate climate change and supports the livelihoods, health and well-being of millions of people around the world. Terrestrial biodiversity faces a number of threats, however, including overexploitation, invasive species and climate change. As a result, species extinctions are currently occurring one thousand times faster than the natural rate. About 30% of land is degraded, leading to declines in agricultural productivity and outputs.
IUCN works to conserve terrestrial ecosystems by assessing species’ extinction risk, improving land use management and restoring degraded landscapes.
SDG 14
Over three billion people depend on coastal and marine biodiversity for food and income. However, coastal, marine and polar ecosystems are under threat from over-exploitation of resources, habitat destruction, pollution and climate change. This has negative impacts on species, ecosystems and ecological processes, reducing fish stocks and increasing extreme weather events and plastic contamination.
IUCN works to ensure that the biodiversity and productivity of coastal, marine and polar ecosystems are restored and maintained, and that their resources are used sustainably and equitably.
SD 11
Natural areas in and around cities provide important benefits and services to society, including climate regulation, disaster risk reduction, and food and water supply. They also support the mental and physical health of urban and rural inhabitants. As cities continue to expand into natural areas, there is an urgent need to secure the continued delivery of these benefits through appropriate urban planning and management approaches.
IUCN works with governments, the private sector and the scientific community to develop and implement cost-effective ‘nature-based solutions’ to urban challenges – actions to protect, sustainably manage and restore ecosystems.
SDG 3
Malnutrition affects the development of children and is an underlying contributing factor in about 45% of all child deaths globally. For many rural and coastal populations, wild, local species can provide the essential nutrients needed for good maternal and child health, reducing the morbidity and mortality of young mothers and children. Nature also provides ingredients used for both modern and traditional medicines. Green spaces in urban areas improve mental and physical health and well-being.
IUCN works to conserve local species, ecosystems, protected areas and urban green spaces for the nutrients, medicinal products, clean air and other services they provide.
https://www.iucn.org/theme/global-policy/our-work/sustainable-development-goals
IUCN Key documents on SDGs
https://www.iucn.org/theme/global-policy/resources/position-papers/sustainable-development-goals
IUCN Commissions
The six IUCN Commissions are broad and active networks of scientists and experts providing IUCN and its Members with sound know-how and policy advice to drive conservation and sustainable development.
https://www.iucn.org/about/union/commissions
Theme © IUCN
IUCN works across a wide range of themes related to conservation, environmental and ecological issue.
https://www.iucn.org/theme/protected-areas
Protected Areas © IUCN
Protected areas are an important line of defense in combatting the twin crises of climate change and biodiversity loss simultaneously.
IUCN Global Protected Areas Programme and IUCN World Commission on Protected Areas. Delivering the Promise of Sydney.
World Commission on Protected Areas © IUCN

The premier network of 2500 experts from 140 countries that mobilizes action in science, conservation, policy, and engagement to support well managed and connected parks and other protected areas. A brief history of IUCN World Commission on Protected Areas.
https://www.iucn.org/commissions/world-commission-protected-areas/our-work
https://www.iucn.org/sites/dev/files/import/downloads/history_wcpa_15july_web_version_1.pdf
https://www.iucn.org/theme/protected-areas/about
https://www.iucn.org/commissions/world-commission-protected-areas
IUCN WCPA Urban Conservation Strategies Specialist Group © IUCN
https://theurbanimperative.org/
IUCN Resolution WCC-2016-Res-029 Adopted by the 2016 IUCN World Conservation Congress in Hawai'i, US "Incorporating Urban Dimensions of Conservation into the Work of IUCN"
https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/resrecfiles/WCC_2016_RES_029_EN.pdf
IUCN WCPA COVID-19 Protected Areas Task Force © IUCN
https://www.iucn.org/commissions/world-commission-protected-areas/our-work/covid-19
IUCN Green List of Protected and Conserved Areas © IUCN
The IUCN Green List of Protected and Conserved Areas is the first global standard of best practice for area-based conservation. It is a programme of certification for protected and conserved areas – national parks, natural World Heritage sites, community conserved areas, nature reserves and so on – that are effectively managed and fairly governed.
59 sites in 16 countries
By giving recognition to well-managed and well-governed protected and conserved areas, the IUCN Green List of Protected and Conserved Areas aims to increase the number of natural areas delivering long-lasting conservation results for people and nature.
https://www.iucn.org/theme/protected-areas/our-work/iucn-green-list-protected-and-conserved-areas
 Photo IUCN ©
Photo IUCN ©
Globally Consistent, Locally Relevant
 Photo IUCN ©
Photo IUCN ©
https://iucngreenlist.org/making-a-difference/sustainable-development-goals/
http://www.iucn.it/pagina.php?id=52
Parchi italiani in Green List, la soddisfazione del ministro Cingolani
"Certificazione di eccellenza al mondo per quanto riguarda la governance delle aree protette"
http://www.iucn.it/dettaglio.php?id=64075
 Photo IUCN ©
Photo IUCN ©
IUCN Congress history © IUCN
https://www.iucn.org/about/world-conservation-congress/congress-history
In the past, Congresses were held every two years, then every three, and now they are held every four years. Initially, the Congress only consisted of the Members’ Assembly of all IUCN member organizations. Since 1996, the Congress has grown to include the Forum, open to all, to debate major sustainable development issues, propose solutions and facilitate the sharing of information and experiences.
The IUCN World Conservation Congress has been held in all corners of the world:
- 2016 Hawaiʻi
- 2012 Jeju
- 2008 Barcelona
- 2004 Bangkok
- 2000 Amman
- 1996 Montreal
- 1994 Buenos Aires
- 1990 Perth
- 1988 San José
- 1984 Madrid
- 1981 Christchurch
- 1978 Ashkhabad
- 1977 Geneva (extra ordinary session)
- 1975 Kinshasa
- 1972 Banff
- 1969 New Delhi
- 1966 Lucerne
- 1963 Nairobi
- 1960 Warsaw
- 1958 Athens
- 1956 Edinburgh
- 1954 Copenhagen
- 1952 Caracas
- 1950 Brussels
- 1948 Fontainebleau
Congress archives © IUCN
https://www.iucn.org/about/world-conservation-congress/congress-archives
Proceedings © IUCN
- 2016 World Conservation Congress, Hawai‘i, USA
- 2012 World Conservation Congress, Jeju, Republic of Korea
- 2008 World Conservation Congress, Barcelona, Spain
- 2004 World Conservation Congress, Bangkok, Thailand
- 2000 World Conservation Congress, Amman, Jordan
- 1996 World Conservation Congress, Montreal, Canada
- 19th General Assembly, 1994 - Buenos Aires, Argentina
- 18th General Assembly, 1990 - Perth, Australia
- 17th General Assembly, 1988 - San Jose, Costa Rica
- 16th General Assembly, 1984 - Madrid, Spain
- 15th General Assembly, 1981 - Christchurch, New Zealand
- 14th General Assembly, 1978 - Ashkhabad, USSR
- 13th (Extraodinary) General Assembly, 1977 - Geneva, Switzerland
- 12th General Assembly, 1975 - Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo
- 11th General Assembly, 1972 - Banff, Canada
- 10th General Assembly, 1969 - New Delhi, India
- 9th General Assembly, 1966 - Lucerne, Switzerland
- 8th General Assembly, 1963 - Nairobi, Kenya
- 7th General Assembly, 1960 - Warsaw, Poland
- 6th General Assembly, 1958 - Athens, Greece
- 5th General Assembly, 1956 - Edinburg, UK
- 4th General Assembly, 1954 - Copenhagen, Denmark
- 3rd General Assembly, 1952 - Caracas, Venezuela
- 2nd Session of the General Assembly, 1950 - Brussels, Belgium
- International Union for Protection of Nature established in Fontainebleau, 5 October 1948
Resolutions and Recommendations* © IUCN
You can access all resolutions and recommendations since 1948:
- IUCN Resolutions and Recommendations Platform (searchable by keyword)
- IUCN Resolutions publications from previous Congresses (pdf format)
- IUCN Resolution publications from previous General Assemblies (pdf format)
Related documents © IUCN
- A review of the impact of IUCN resolutions on international conservation efforts
- 2012: A study to develop monitoring for results of IUCN Resolutions and Recommendations
* Resolutions and Recommendations are decisions adopted by IUCN Members at the World Conservation Congress/General Assembly.
Motions** © IUCN
You will find below motions as submitted to previous Congresses:
- All motions from previous Congresses in online library (pdf format)
- Motions from Congresses prior to 2000 are not available in electronic format
** Motions are draft decisions submitted by IUCN Members for consideration at the World Conservation Congress/General Assembly.
©2021 IUCN, International Union for Conservation of Nature

